Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
Microsoft SQL Server is a cloud-ready enterprise database server, it comes in versions and editions.
The recent versions of SQL server are named by the year of issue: SQL Server 2016, SQL Server 2014, and SQL Server 2012.
Microsoft SQL Server 2016 SP1 is the most recent version for production.
The latest Public Preview version is vNext CTP 1.3 (February 2017) (Community Technology Preview, vNext means the next version of Microsoft products before it will be given the official name).
SQL Server is backwards compatible. A database created by a more recent version of Microsoft SQL Server cannot be attached or restored to an earlier version with standard methods. Also Microsoft has a restriction to jump forward to versions. SQL Server 2016 supports upgrade from the SQL Server 2008 SP3 or later, SQL Server 2008 R2 SP2 or later, SQL Server 2012 SP2 or later and SQL Server 2014 or later versions.
Each version of SQL Server has several Editions, the most used editions – Enterprise, Developer, Standard, Express and Web.
The Enterprise Edition is the most powerful edition of SQL Server often used by corporations; it's fully functional. Enterprise edition is available in the 180 days Trial (Evaluation) version. The Developer Edition is free full-featured set of Enterprise edition, you can use it for testing purposes.
Most people who work with databases use the SQL Server Management Studio tool (SMSS). It has a graphical user interface for creating databases and the objects in the databases. Management Studio also has a query editor which allows to create and run scripts containing Transact-SQL statements. Management Studio can be installed from the SQL Server installation disk, or downloaded directly from MSDN. Since SQL Server 2016 SSMS is a standalone tool, now is easy to install it, check and manage the tools updates.
SSMS can be used to develop and work with several installations and instances of SQL Server in one application. These installations can be on one computer or on multiple computers connected through the local area network (LAN) and the wide area network (WAN) and also to the cloud (Azure). So you can work with different instances of SQL Server from one instance of SSMS.
It can be run Start->All apps->Microsoft SQL Server 2016(or another version)->SQL Server Management Studio.
Use Management Studio to:
- connecting to an instance of the Database Engine, attaching/detaching databases;
- creating, alerting or deleting different database objects (databases, tables, cubes, database users, and logins);
- performing backups with built-up backup tools;
- reporting on server performance and monitoring sever activity;
- configuring the database engine properties.
SQL Server Management Studio is built upon the Visual Studio Isolated Shell, it supports extensibility (add-ins/plug-ins). There are a lot of free and commercial add-ins which can help you in your work.
Microsoft provides samples of databases in each version of SQL Server. By default, sample databases and sample code are not installed as part of SQL Server Setup. Prior to SQL Server 2016 version the samples can be downloaded from CodePlex http://msftdbprodsamples.codeplex.com/.
Also Microsoft SQL Server 2016 has a new sample database called Wide World Importers. The WWI code samples are located in the GitHub https://github.com/Microsoft/sql-server-samples/releases/tag/wide-world-importers-v1.0
After the downloading the backup of samples you need to restore it on your instance.
Move the backup file (*.bak) to a location on your local server to Backup folder. In case of installing SQL Server with default settings the path to the Backup folder will be:
<disk>:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.<Instance_name>\MSSQL\Backup for SQL Server 2012 version
<disk>:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.<Instance_name>\MSSQL\Backup for SQL Server 2014 version
<disk>:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.<Instance_name>\MSSQL\Backup for SQL Server 2016
<disk>:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.<Instance_name>\MSSQL\Backup for SQL Server vNext (current test version)
The default Instance name is MSSQLSERVER.
You can restore/backup or attach/detach the database using the SSMS user interface or with using the T-SQL query.
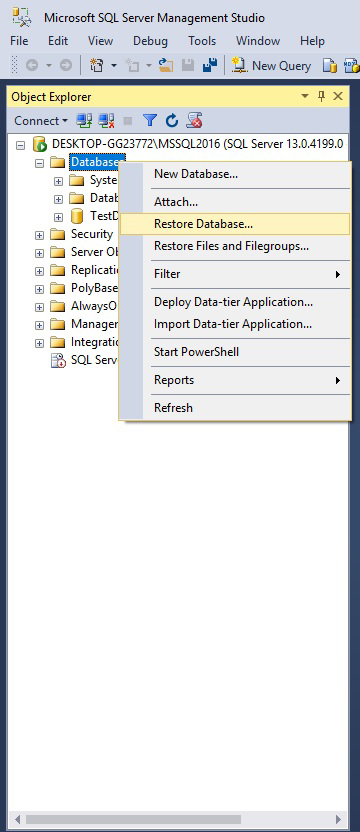
To restore the database using the SSMS:
Right click on Databases, choose Restore database
On General Page choose the path to backup file
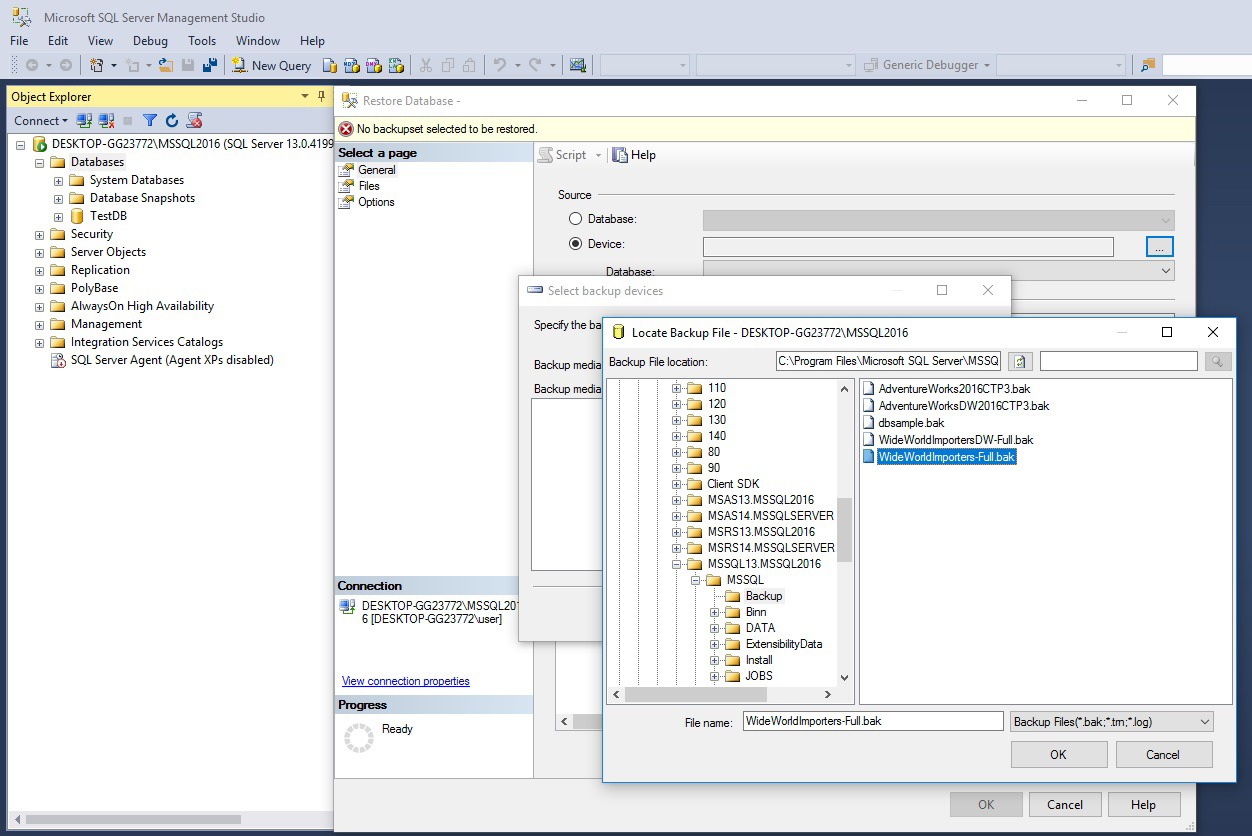
Choose the file and click OK on each page.
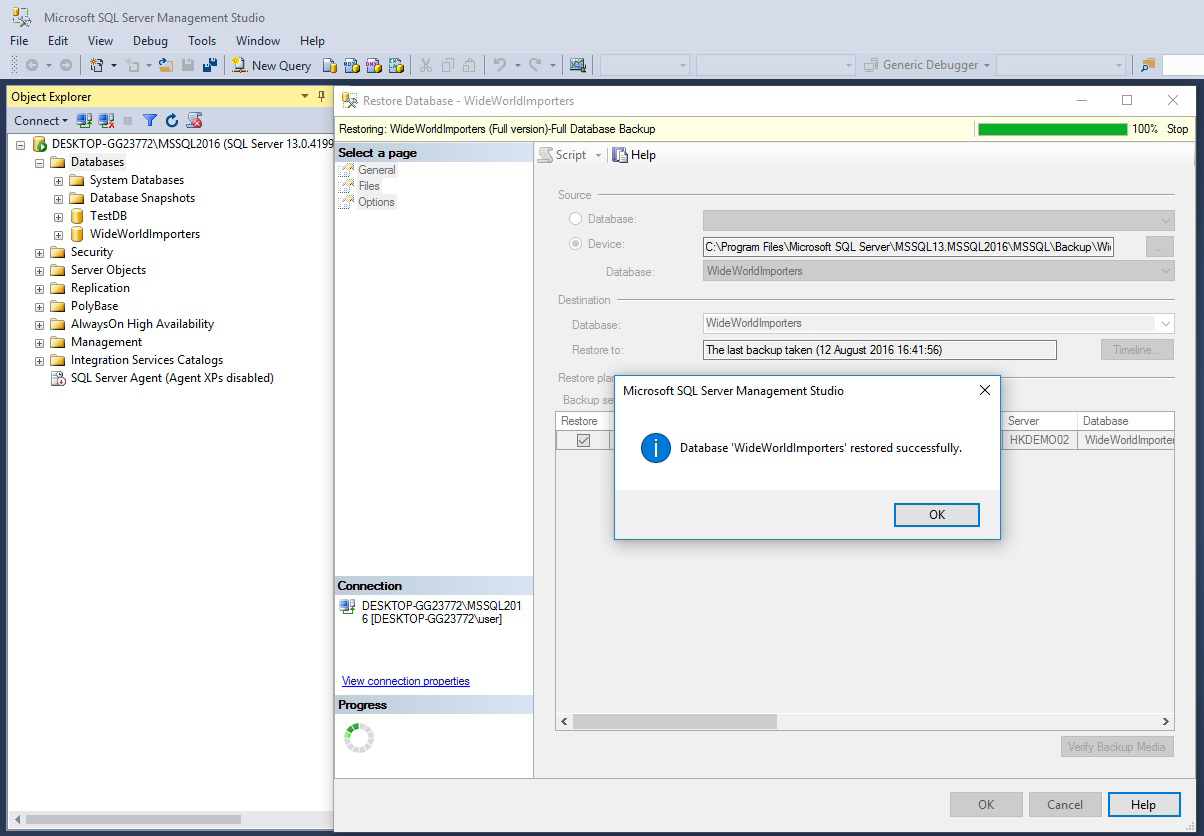
Press OK.
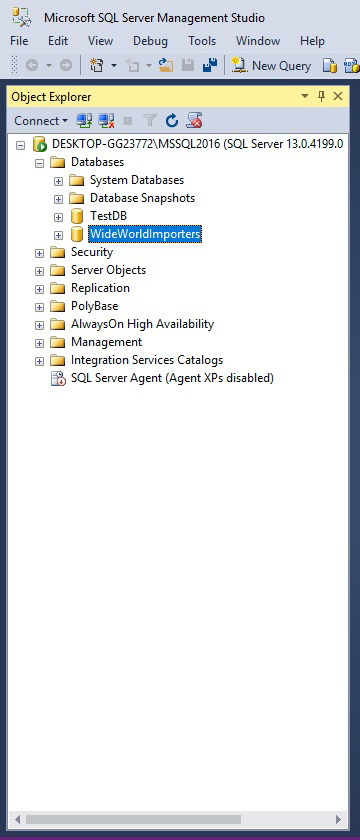
You will see the restored database in Object Explorer:
As an alternative you can restore the database with T-SQL query.
Click the ‘New query’ button in SSMS Object Explorer and enter the following into your query window
(Script for restoring WideWorldImporters backup on SQL Server 2016):
USE [master] RESTORE DATABASE WideWorldImporters FROM disk= 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\WideWorldImporters-Full.bak' WITH MOVE 'WWI_Primary' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\WideWorldImporters.mdf', MOVE 'WWI_UserData' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\WideWorldImporters.ndf', MOVE 'WWI_Log' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\WideWorldImporters.ldf', MOVE 'WWI_InMemory_Data_1' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\WWI_InMemory_Data_1' ,REPLACE
Script for restoring AdventureWorks2014 on SQL Server 2014:
USE [master] RESTORE DATABASE AdventureWorks2014 FROM disk= 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\AdventureWorks2014.bak' WITH MOVE 'AdventureWorks2014_data' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\AdventureWorks2014.mdf', MOVE 'AdventureWorks2014_Log' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\AdventureWorks2014.ldf' ,REPLACE
If you are using T-sql queries to restore the databases, you should to replace the file path with your own and change the file name if it needed.
If you need to know the logical names of database files for using in restoring procedure you may use RESTORE FILELISTONLY, for example:
RESTORE FILELISTONLY FROM DISK='C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\AdventureWorks2014.bak'
If you have the database files (like AdventureWorks2014 _Data.mdf and AdventureWorks2014 _Log.ldf) use the attach method.
To attach the database using the SSMS user interface:
Right click on Databases, choose Attach...
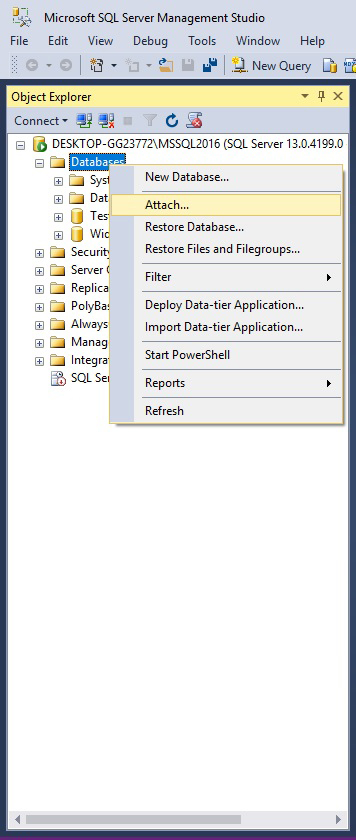
and choose the path to database files
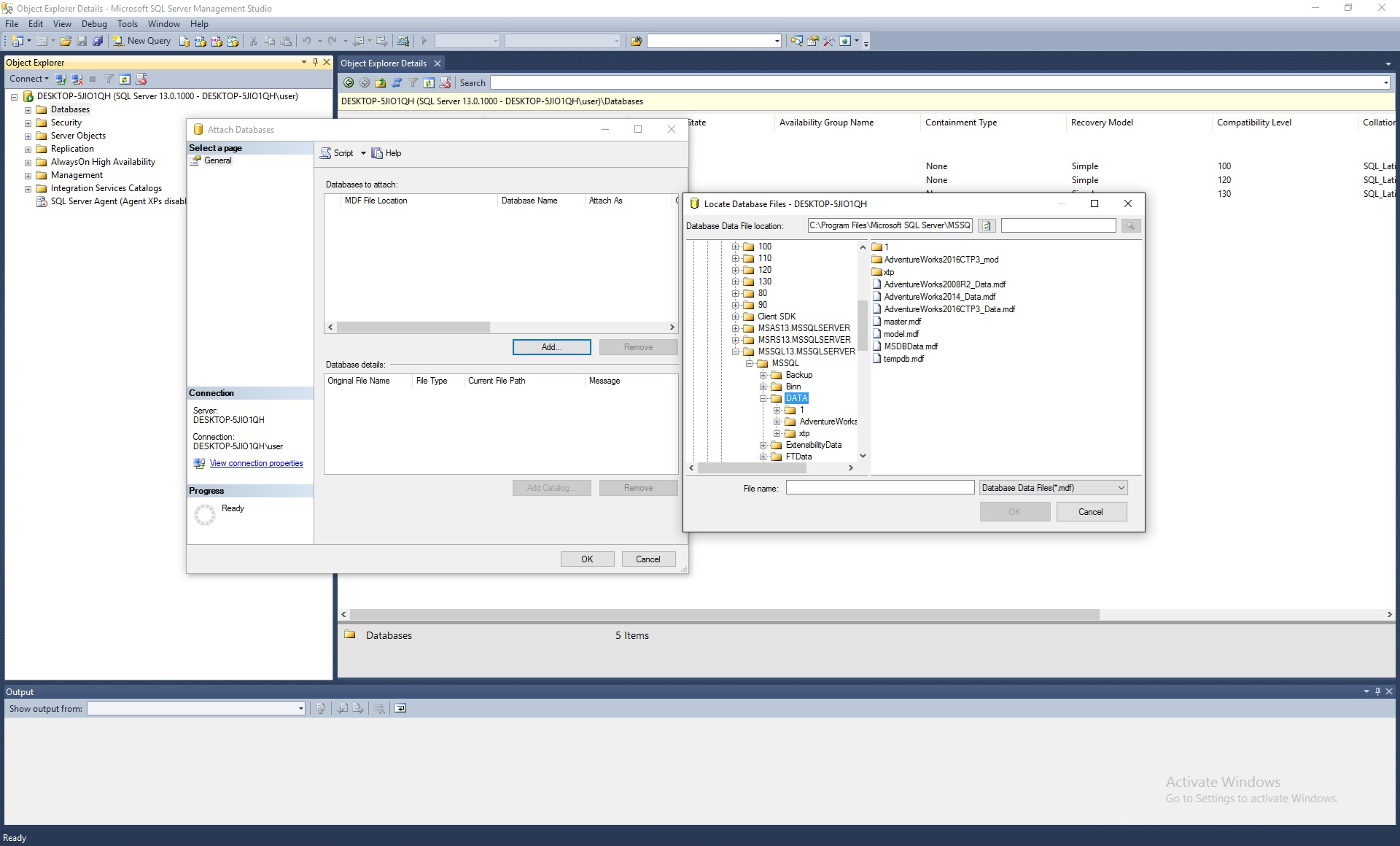
Click Ok to confirm.
To attach the database using the T-sql
(for SQL Server 2014 and AdventureWorks2014):
USE [master] CREATE DATABASE AdventureWorks2014 ON (FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\AdventureWorks2014_Data.mdf'), (FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\AdventureWorks2014_Log.ldf') FOR ATTACH;
It also may be needed to change the path in the query.
Now you can work with Microsoft samples of databases. The Microsoft database samples are the good example of the database normalization and using of naming convention. The main idea of normalization is that the tables that contain repeated information should be divided into separate tables to eliminate the duplicates. It does not exist a naming convention database objects published by Microsoft, and you can choose your preferred style for naming objects (for example "PascalCase" or "camelCase" or using of underscore "_", usually it's regulated by corporate rules).
Now you can access the databases using a specific SQL statements.